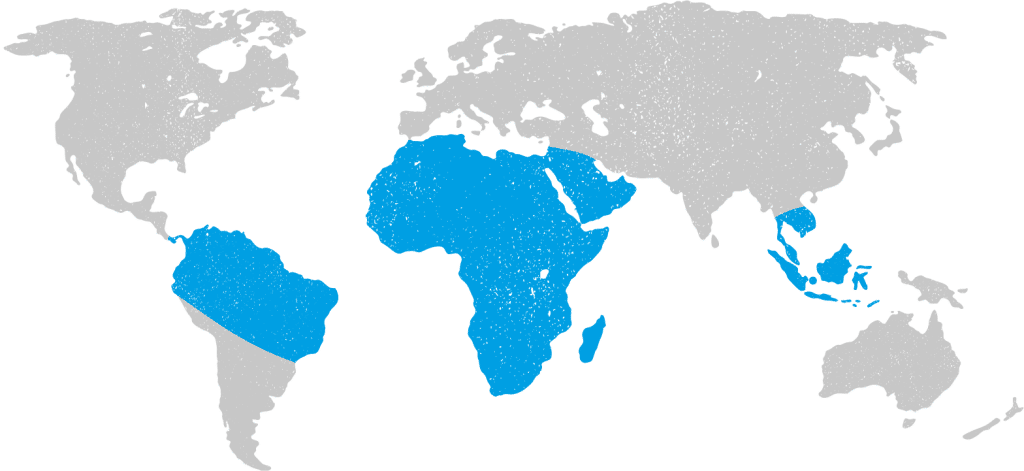
Schistosomiasis, also known as Bilharzia, is a parasitic disease caused by flatworms. The larvae of these parasites are released into freshwater by infected snails. When people come into contact with untreated water—such as lakes and rivers—the larvae can penetrate the skin and migrate to the lungs and liver, where they mature into adult worms.
These adult worms lay eggs in the blood vessels around the bladder or intestines, which can cause significant health issues. Schistosomiasis often presents no symptoms initially, which means it can remain undetected for months or even years, leading to serious complications.
The disease is contracted through direct skin contact with contaminated freshwater. Activities such as swimming, bathing, wading, or participating in water sports in affected rivers, lakes, or streams increase the risk. Schistosomiasis is not contracted in saltwater environments like the sea.
Currently, there is no vaccine or specific drug available to prevent Schistosomiasis. To reduce your risk:
For those traveling to risk areas, taking these precautions can help protect against Schistosomiasis and other waterborne diseases.