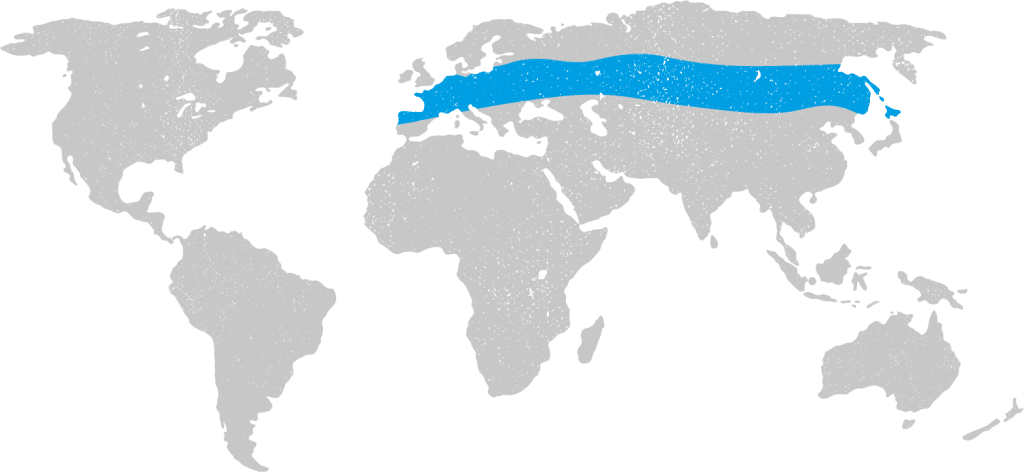
Tick-Borne Encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infection transmitted primarily through the bite of an infected tick. In rare cases, it can also be contracted from consuming unpasteurised milk from infected cows, sheep, or goats.
Travellers who are likely to walk, camp, or work in grassy or wooded areas for extended periods, especially during the spring, summer, and autumn months when ticks are most active, are at higher risk. These environments provide ideal conditions for ticks to thrive and transmit the virus.
The initial symptoms of Tick-Borne Encephalitis resemble those of the flu and may be followed by neurological complications. Early signs include fever, headache, and muscle aches, which can progress to more severe symptoms affecting the central nervous system.
Taking these precautions can significantly reduce your risk of Tick-Borne Encephalitis and help you stay safe during your outdoor adventures.
| Age of use | Doses required | Schedule | Time Before Travel | Booster Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 years+ | 2 | 0, 1-3 months | Last dose 2 weeks before* | 5-12 months |
| Age of use | Doses required | Schedule | Time Before Travel | Booster Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-15 years | 2 | 0, 1-3 months | Last dose 2 weeks before* | 5-12 months |
*Vaccines work best if given time to become active. This vaccine can be given up to the day before travel and will provide some cover.